Affect of Change in Demand on equilibrium
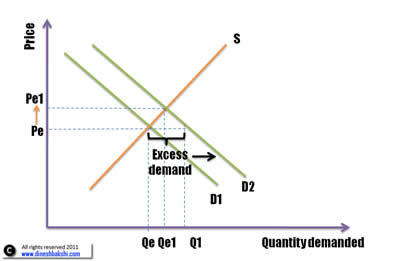
If there is a shift in demand, it will lead to a movement along the supply curve and a new equilibrium point will be achieved.
In figure 1, There is equilibrium at point E, where the price is Pe and quantity supplied is Qe. There is a shift in demand from D1 to D2. At price Pe, it will lead to a 'excess demand' situation (F). In order to cope with excess demand the suppliers will start increasing the price and more will be supplied. On the other hand as the prices increase, demand will start to fall. This phenomenon will continue till a new equilibrium stage is reached at point G. Now the Price will be P1 and quantity supplied at that point will be Qe1. Hence it has resulted in an increase in price and quantity demanded.
The opposite will happen if there is a shift of demand curve to the left. The price and quantity demand will fall.
Affect of Change in Supply on equilibrium
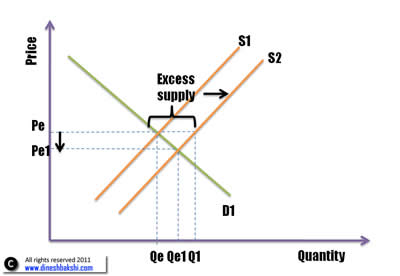
In figure 2, the equilibrium point is E with Pe as the equilibrium price and Qe as the quantity demanded. Now there is a rightward shift in supply curve to S2 i.e. supply increases. This will lead to a excess supply. Producers will find it difficult to find consumers and will have to reduce their prices to clear their inventories. As the prices fall, more people will be interested in buying the product. This will continue till equilibrium is achieved at G. There will a price fall from Pe to Pe1 and Qe to Qe1. The result is lower equilibrium price and lower equilibrium quantity.
Watch a Video





