Economic growth
Economic growth is the increase of per capita gross domestic product (GDP) or other measure of aggregate income, typically reported as the annual rate of change in real GDP.
Economic growth is primarily driven by improvements in productivity, which involves producing more goods and services with the same inputs of labor, capital, energy and materials.
Economic Development
Economic development is the increase in the standard of living in a nation's population with sustained growth from a simple, low-income economy to a modern, high-income economy. Also, if the local quality of life could be improved, economic development would be enhanced. Its scope includes the process and policies by which a nation improves the economic, political, and social well-being of its people.
Sources of economic growth in economically less developed countries
- Natural factors
- Improving the quality of human capital through education and training
- Improving the quantity physical capital
- the development and use of new technologies that are appropriate to the conditions of the economically less developed countries
- Improving the Institutional factors such as banking system, legal system, education system, political stability etc.
Common characteristics of economically less developed countries
- Low standards of living, low GDP per capita, low incomes, inequality, poor health, inadequate education
- Low level of productivity
- High rates of population growth, High birth rates and dependency burden
- High and rising levels of unemployment and underemployment
- Substantial dependence on agricultural production/primary sector
- Prevalence of imperfect markets i.e. Lack of banking, legal system, adequate infrastructure, imperfect information.
- Dominance by developed nations and dependence in terms of international relations.
Sources of economic development
- Education leads to more gender equality, improved levels of health
- Health care coupled with education facilities improve the quality of workforce, leading to increase in productivity
- Infrastructure :better facilities and services such as roads, transport, communication
- Political stability
Poverty Trap
Some countries there may be communities caught in poverty trap (poverty cycle) where poor communities are unable to invest in physical, human and natural capital due to low or no savings; poverty is therefore transmitted from generation to generation, and there is a need for intervention to break out of the cycle.
The diagram below illustrates a poverty trap
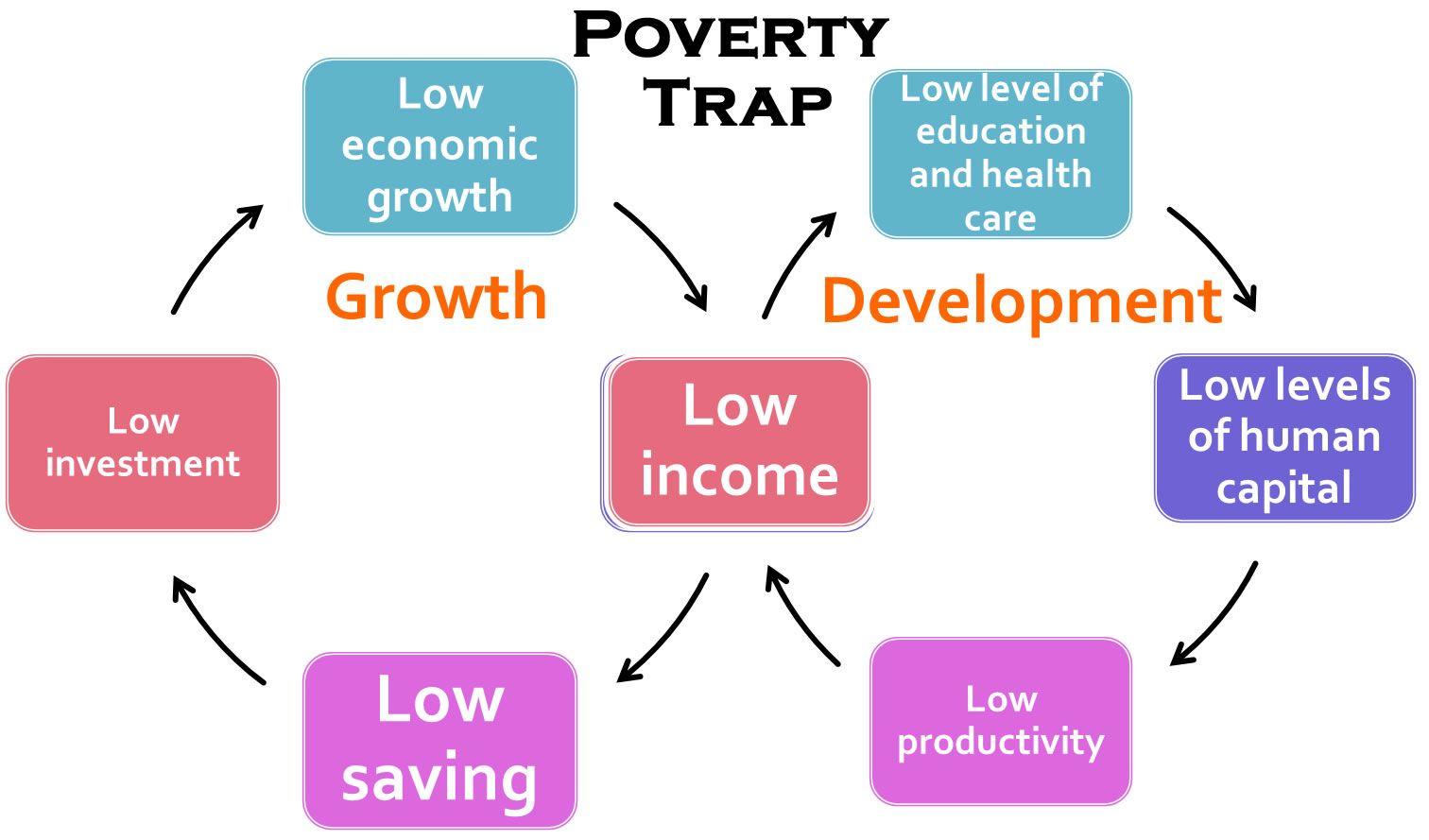

In order to escape the poverty trap, it is argued that individuals in poverty must be given sufficient aid so that they can acquire the critical mass of capital necessary to raise themselves out of poverty. This theory of poverty helps to explain why certain aid programs which do not provide a high enough level of support may be ineffective at raising individuals from poverty. If those in poverty do not acquire the critical mass of capital, then they will simply remain dependent on aid indefinitely and regress if aid is ended.
Diversity among economically less developed nations
- Economically less developed countries differ enormously from each other in terms of
- Resource endowment may differ.
- Historical background: Most have been colonized.
- Geographic and demographic factors
- Ethnic and religious breakdown
- Structure of industry: some may heavily depend on primary sector while other may not.
- Per capita income levels may differ in these countries.
- Political structure : These countries might be having different political structure, Some may be having democracies, monarchies, military rule, single party states and so on.
International development goals
The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) are eight international development goals that were officially established following the Millennium Summit of the United Nations in 2000, following the adoption of the United Nations Millennium Declaration. All 193 United Nations member states and at least 23 international organizations have agreed to achieve these goals by the year 2015. The goals are:
-
eradicating extreme poverty and hunger,

- achieving universal primary education,
- promoting gender equality and empowering women
- reducing child mortality rates,
- improving maternal health,
- combating HIV/AIDS, malaria, and other diseases,
- ensuring environmental sustainability, and
- developing a global partnership for development





