Product Life Cycle
A Product life cycle shows the different stages through which a product goes from development to decline.
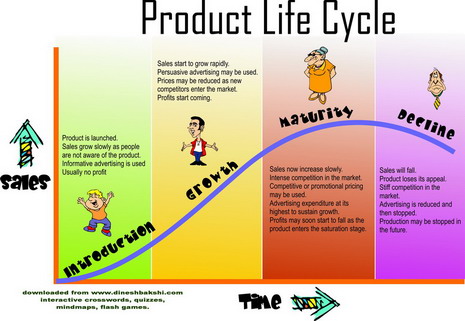
Introduction Stage
- Product launched into the market.
- Sales grow slowly.
- Informative advertising is done.
- Firm might not earn a profit at this stage.
- Price skimming may be used if the product is new invention and has no competitors.
- Competitive pricing may be used if it already has lot of competitors.
Growth Stage
- Sales grow rapidly.
- Persuasive advertising may be used.
- Prices may be reduced if faced by stiff competition.
- Firm starts earning profits.
Maturity Stage
- Sales increase slowly and reach the highest sales figures.
- Competition is at the maximum level as many new ‘me too’ products may be in the market.
- Promotional pricing might be a good option.
- Profits are at the highest level as the firm is also getting economies of scale.
- Repetitive advertising is done to remind the consumers.
Saturation Stage
- Sales are stagnant.
- Maximum competition but no new competitors and the market is already crowded with the same types of products.
- Promotional pricing or competitive pricing may be a good choice.
- Advertising efforts at its highest point.
Decline Stage
- Sales start to decline.
- Profits start to come down.
- Marketing research it done to find out whether this decline is permanent or temporary. If the decline is permanent in nature then stop the production of the product, otherwise implement extension strategies.
- Advertising is reduced.
Extension stage
- Introduce new variations of the original product
- Try to sell the product in different markets.
- Make small changes in the colour, design or packaging
- Start a new advertising campaign.
- Add more retail outlets to boost sales.





