Sources of finance
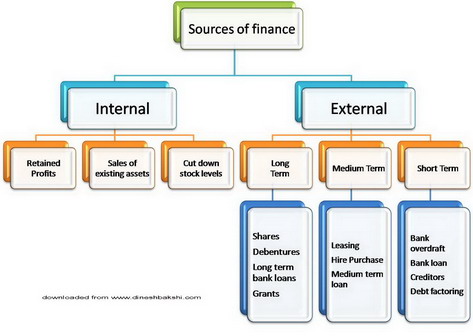
A business might have access to various sources of financing its needs. These sources of finance can be classified as:
Internal and external
Internal Sources of finance
this is money raised from inside the business. It includes
Sales of assets: Business might sell off old, obsolete assets which are no longer used by the business to raise additional cash for the business.
Advantage |
Disadvantage |
|
Better use of capital |
A new business might not have any old or obsolete assets |
Retained profits: Businesses (especially limited companies) usually keep some part of the profit every year for future use. This is also known as ploughed back profit. Over a period of time it can total up to a huge amount which can be used for financing the business.
Advantage |
Disadvantage |
|
Does not increase liabilities |
Not available to new businesses |
Reduction in working capital: Cutting the stock levels can also help the business to raise additional cash.
Advantage |
Disadvantage |
|
Costs related to storage of stock is reduced |
May lead to shortage of stock and loss of sales |
External Sources of Finance
This is the money raised from outside the business. It includes
Short Term
Bank overdraft: Bank overdraft is a facility given by banks to its business customers, people having current accounts. Through this facility the customers can overdraw their accounts to a greater value than the balance in the account. To overdrawn amount is agreed in advance with the bank manager. The bank assigns a limit to overdraw from the account and the business can meet its short term liabilities by writing cheques to the extent of limit allowed.
Advantage |
Disadvantage |
|
|
Trade Credit: Usually in business dealing supplier give a grace period to their customers to pay for the purchases. This can range from 1 week to 90 days depending upon the type of business and industry.
Advantage |
Disadvantage |
|
No interest has to be paid. |
The business may not get cash discounts. |
By delaying the payment of bills for goods or services received, a business is, in effect, obtaining finance which can be used for more important expenditures.
Factoring of debts: It involves the business selling its bills receivable to a debt factoring company at a discounted price. In this way the business get access to instant cash.
Click on these links to know more about debt factoring
Factoring of debts
Advantages and Disadvantages of debt factoring
Medium Term
Hire purchase: It involves purchasing an asset paying for it over a period of time. Usually a percentage of the price is paid as down payment and the rest is paid in installments for the period of time agreed upon. The business has to pay an interest on these installments.
Leasing: Leasing involves using an asset, but the ownership does not pass to the user. Business can lease a building or machinery and a periodic payment is made as rent, till the time the business uses the assets. The business does not need to purchase the asset.
Advantage |
Disadvantage |
|
|
Medium term bank loan: A bank loan for 1 year to 5 years.
Long term
Long term Bank loan: borrowing from bank for a limited period of time. The business has to pay an interest on the borrowing. This interest may be fixed or variable. Businesses taking loan will often have to provide security or collateral for the loan.
Issue of share: It is a permanent source of finance but only available to limited companies. Public limited companies can sell further shares up to the limit of their authorized share capital. Private limited companies can sell further shares to existing shareholders.
Advantage |
Disadvantage |
|
Permanent source of capital. |
Dividends have to be paid to the shareholders. |
Debentures: A debenture is defined as a certificate of acceptance of loans which is given under the company's stamp and carries an undertaking that the debenture holder will get a fixed return (fixed on the basis of interest rates) and the principal amount whenever the debenture matures. It is issued for a long periods of time. Debentures are generally freely transferable by the debenture holder. Debenture holders have no voting rights and the interest given to them is a charge against profit.
Sales and lease back: this involves a firm selling its assets or property to an investment company and then leasing it back over a long period of time. The business thus can use the asset without purchasing it and can use the revenue earned from its sale for other purposes.
Micro-Finance: Micro-finance is the provision of financial services to low-income people. It refers to a movement that envisions a world where low-income households have permanent access to high-quality and affordable financial services to finance income-producing activities, build assets, stabilize consumption, and protect against risks. Initially the term was closely associated with microcredit—very small loans to unsalaried borrowers with little or no collateral—but the term has since evolved to include a range of financial products, such as savings, insurance, payments, and remittances.
Typical microfinance clients have low incomes and are often self-employed in the informal economy, conditions that together typically deny them access to banks and other formal financial institutions. They commonly run small stores or street stalls, create and sell items they make in their homes, and in rural areas, microfinance clients may be small-scale farmers and those who process or trade crops and goods.
Microfinance clients are often just below or above the poverty line, commonly defined as earnings of US$1.25 a day, and women constitute a majority of borrowers. Over the past decades, financial institutions have been developing a range of products to meet the diverse needs of this broad and underserved market.
Crowd Funding: Crowdfunding is the practice of funding a project or venture by raising monetary contributions from a large number of people. today often performed via Internet-mediated registries, but the concept can also be executed through mail-order subscriptions, benefit events, and other methods.
The crowdfunding model is based on three types of actors: the project initiator who proposes the idea and/or project to be funded, individuals or groups who support the idea, and a moderating organization (the "platform") that brings the parties together to launch the idea.
Watch a Video





