Economic growth
What is economic growth?
Economic growth is the increase in the amount of the goods and services produced by an economy over time
Causes of economic growth
The following factors can help to achieve economic growth
Capital accumulation
Investment in capital equipment that is used by people at work is the key to economic growth. These resources will enable the workforce to produce consumer goods more efficiently.
Technological Progress
Improvement in technology will lead to more goods being produced from available resources. The country will have achieved a higher gross domestic product.
Improvement in quality of human resources
Improving the quality of existing workforce can lead to increased productivity and hence optimum utilisation of resources. The quality of human resource can be improved with education, training and healthcare.
Research and development
Discovering new sources of natural resources will add to the total output of the country.
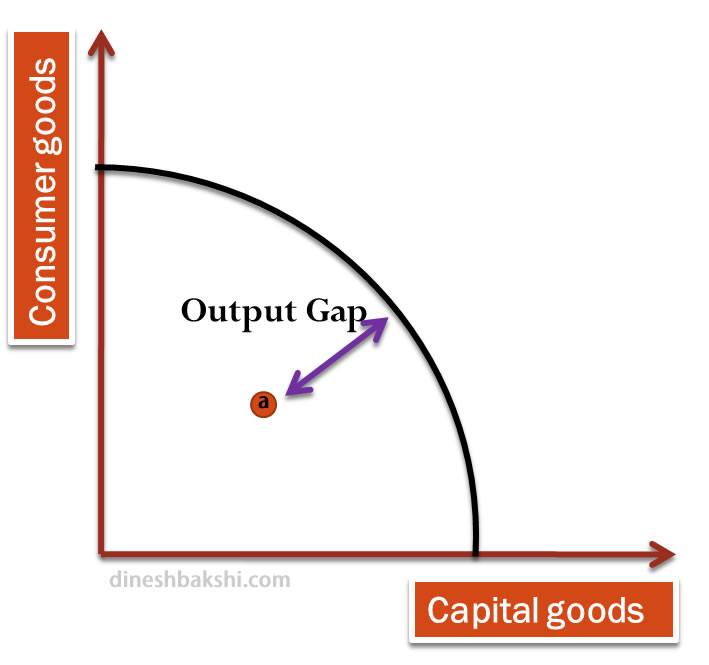
Illustrating Economic growth using a PPC diagram
In case when the economy is operating with a deflationary gap. This means that the economy’s resources are not being fully utilised.

Point ‘a’ indicates a point where the economy is operating inside the PPC. With the economy achieving economic growth it would be equivalent to the movement from ‘a’ to ‘b’.
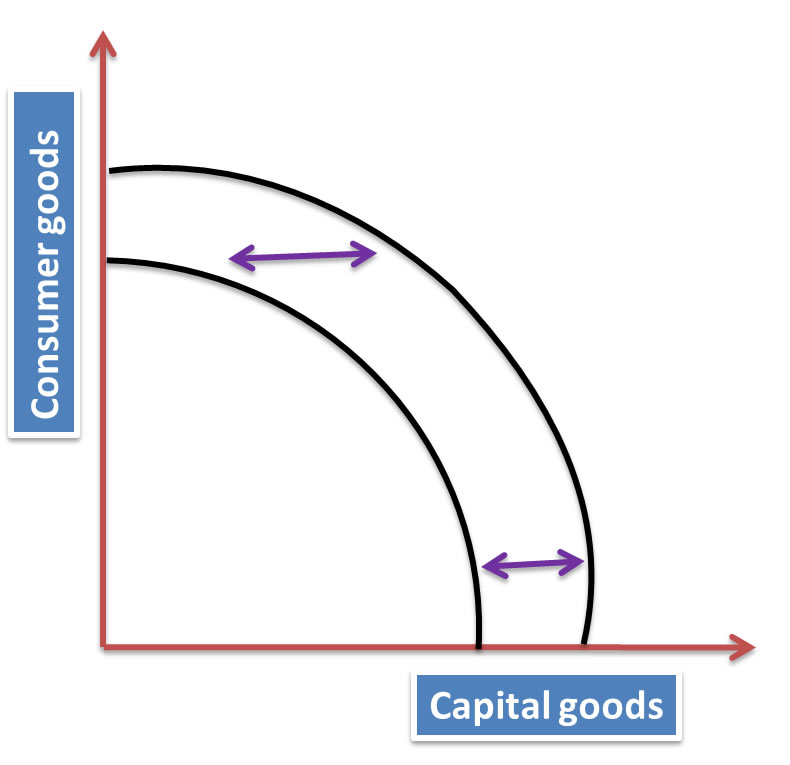
Economic growth can also be achieved by increasing the potential output. This is achieved through supply side policies.
As illustrated by the diagram the outward shift in the PPC signifies the increase in full employment level of output.
Illustrating Economic Growth using a AS/AD diagram
An economy operating below full employment level of output can be illustrated by the diagram. Where the gap between Y1 and Yf signifies deflationary gap.
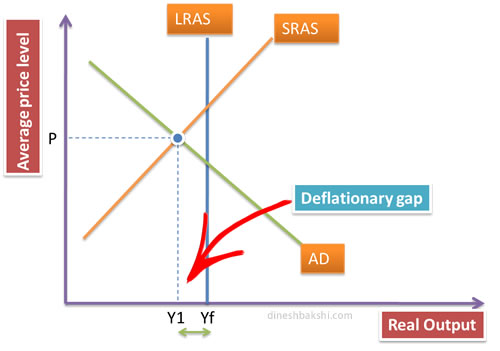

The movement of AD to the right (or increase in Aggregate Demand) will result in filling up of the deflationary gap and the economy will achieve full employment level of output. This is known as economic growth.
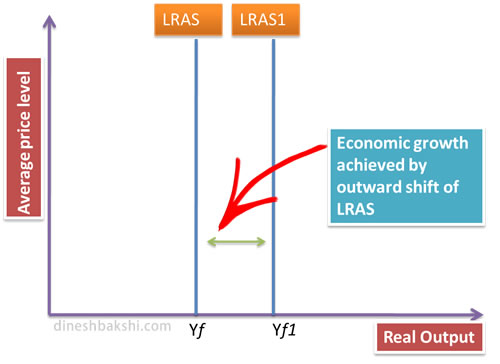
Economy can also achieve economic growth in the long term by increasing the potential output by increasing the efficiency of its factors of production. This can be illustrated by the movement of LRAS to the right. i.e. LRAS1 to LRAS2. This is achieved by government’s supply side policies.
Consequences of economic growth
Positive
- Broadly speaking economic growth will result in the increase in living standard of the population.
- Increase in GDP (more precisely, GDP per capita) will result in the increase in the standard of living of its population.
- Greater income results in higher tax revenue for the government which can be spend of merit and public goods, again a higher living standard.
- An important factor which leads to economic growth is technology. Improved technology results in making our lives easy and comfortable.
- Economic growth leads to higher level of education and health service. This will result in a better social structure with a more stable political setup.
Negative
- Economic growth may not necessarily reflect the quality of life of the population. People may have more material gains at the cost of sacrificing leisure time and neglect of personal relationships.
- Economic growth leads to structural change in the economy, which might result in structural unemployment and income inequalities
- Environment may suffer due to high level of economic activities. High emissions of greenhouse gases are usually associated with economies achieving rapid economic growth.
Calculation of Rate of Growth [HL]






