Aggregate supply (AS)
Aggregate supply is the total amount of goods and services that all industries in the economy will produce at every given price level.
Short run and Long run in Macroeconomics
Short run is the period of time during which the nominal prices of resources, particularly labour (wages) do not change in response to the changes in price level.
Long run is the period of time in which the nominal prices of all resources, including the price of labour (wages), change so as to reflect fully any change in the price levels.
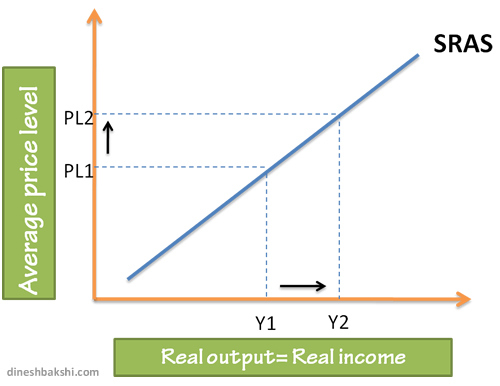
Short Run AS (SRAS) curve
AS curve is similar to a microeconomic supply curve. It is upward sloping and hence has a positive relation between price level and amount of output.
Movement along the SRAS
A change in price level will lead to a movement along the SRAS curve.
Shift of SRAS
Any factor changes other than price level will lead to a shift in SRAS. A rightward shift of SRAS means an increase in Aggregate supply at any particular price level. An leftward shift of SRAS signifies a decrease in Aggregate supply for any particular price level.
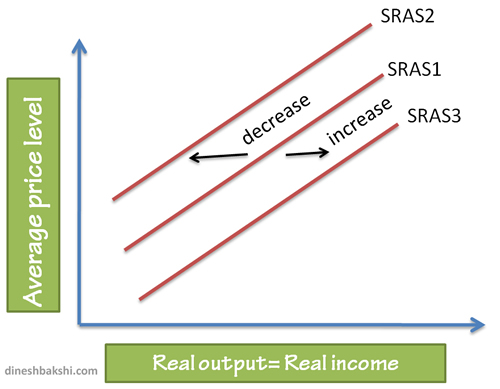
Factors causing a shift of SRAS
Any factor which causes a change in the cost of production will result in a shift of SRAS curve. These factors are
Changes in wages: Wages constitute a major part of the cost of production. As wages increase the cost of production increases and thus the SRAS will move leftward.
Price of raw material: An increase in price of raw material will result in the cost of production going up and thus the SRAS will shift to the left.
Change in Taxes: Increased taxes add to the cost of production and thus SRAS moves leftwards.
Changes in Subsides: If subsidies are provided, this will result in the lowering of cost of production and increase Aggregate supply. Thus SRAS will move rightward.
Change in price of imports: An increase in price of imported components will lead to a increase in price of goods which use a lot of imported components. This will lead to a fall in AS
Long run AS curve
There are two major views relating to the shape of the LRAS. The different beliefs about the shape of the LRAS curve lie at the basis of controversies about appropriate policies to be followed by governments.
The new-classical view (monetarist or free market view)
These economists argue that the LRAS curve does not respond to changes in AD in the long run and is determined completely independently of demand.
According to New classical economist the economy operates at full level of output. Potential output of economy depends on productivity of factors of production rather than price level.
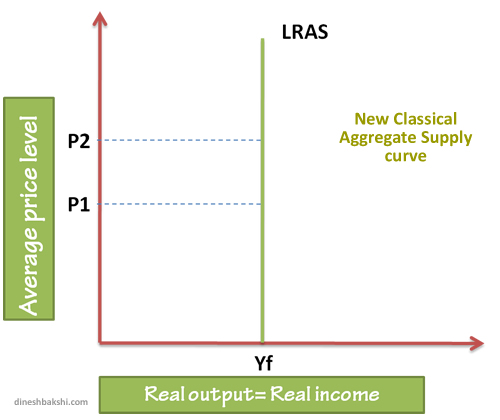
The LRAS curve is vertical at potential GDP, or full employment level of real GDP. This indicates that an expansion of AD will always lead to demand-pull inflation and will not, in the long run, lead to growth in output and thus employment.
The new-classical economists argue that national output may only be increased by adopting supply-side policies to shift the LRAS to the right.
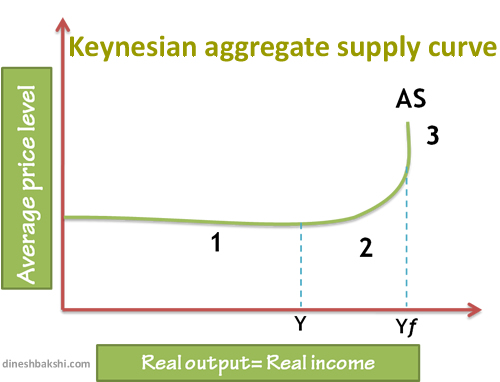
The Keynesian view (interventionist view)
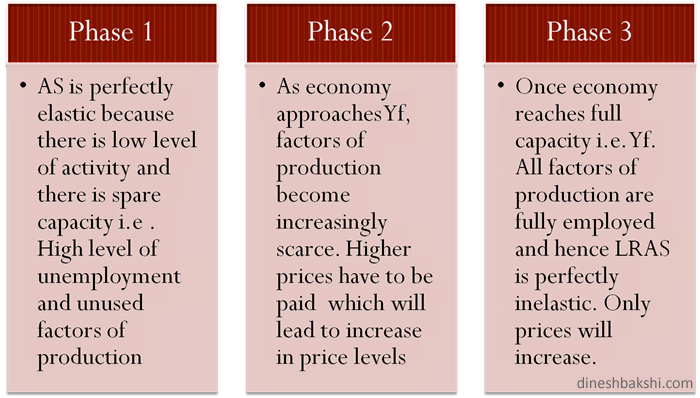
The shape of the curve that is known as the Keynesian LRAS shows three possible phases.