What is economic integration?
Economic integration refers to trade unification between different states by the partial or full abolishing of customs tariffs on trade taking place within the borders of each state.
This is meant in turn to lead to lower prices for distributors and consumers (as no customs duties are paid within the integrated area) and the goal is to increase trade.
What is a trade agreement?
A trade agreement is a contract/agreement/pact between two or more nations that outlines how they will work together to ensure mutual benefit in the field of trade and investment.
Trade agreements are often regional, involving only a relatively small number of countries.
Trade agreements are either bilateral, involving only two countries, or multilateral, involving more than two countries.
What is a trade bloc?
A trade bloc is a type of intergovernmental agreement, where regional barriers to trade, (tariffs and non-tariff barriers) are reduced or eliminated among the participating states.
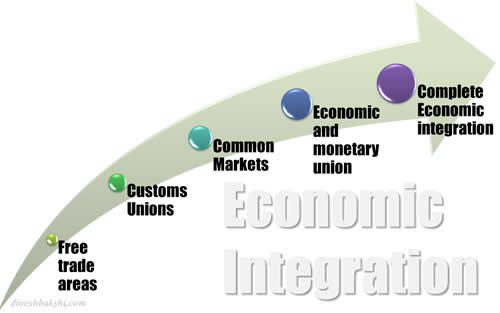
Types of trade blocs
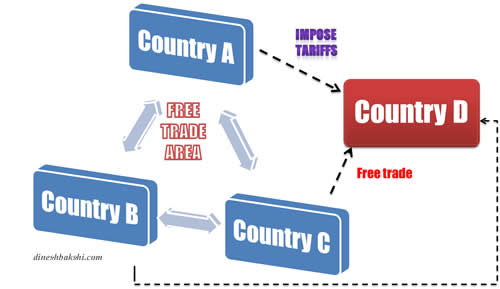
Free Trade Areas
Group of countries agree to eliminate trade barriers.
However they are free to trade with countries outside of the free trade area
Examples NAFTA, ASEAN, SAARC
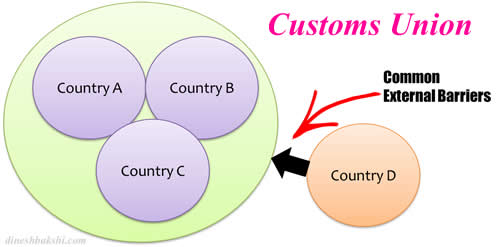
Customs Union
An agreement among countries to have free trade among themselves and to adopt common external barriers against any other country interested in exporting to these countries
Examples European Union, East African Community (Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania], Mercosur [ Brazil, Argentina, Uruguay, Paraguay and Venezuela]
Common Market
A type of custom union where there are common policies on product regulation, and free movement of goods and services, capital and labour.
Best known example is EU
All common markets and economic and monetary unions are also customs unions
Economic & Monetary Unions
A common market with common currency
Where more than two countries use the same currency.
Example Euro
Advantages of single currency
- Reduces the level of transaction cost.
- When trading among each other the countries need not worry about possible exchange rate fluctuations.
- It is easier to make price comparisons between countries.
- Greater FDI is attracted because of reduced transactions costs, reduced uncertainty and the large size of single currency market.
Disadvantages of single currency
- Individual countries lose the ability to set interest rates.
- Individual countries cannot depreciate or devalue its currency value.
- Huge cost involved such as physical changing, reprogramming computers, producing new price lists etc.
Complete Economic Integration
Individual countries have no control of economic policy, full monetary union and complete harmonization of fiscal policy.
Evaluation of Economic integration
- Greater size of the market
- Potential for exports
- Greater efficiency
- More choice
- Lower prices for consumers
- Increased foreign investment
- Greater political stability
- Free trade among members but discriminatory policies against non-members which might not lead to global economic integration.





