Monopsony in the labour market
What is Monopsony?
A Monopsony occurs in the labour market when there is a single dominant buyer of labour. In such a situation this monopoly buyer is the price setter for labour.
Monopsony is the buyer’s counterpart of monopoly. Monopoly means a single seller; Monopsony means a single buyer.
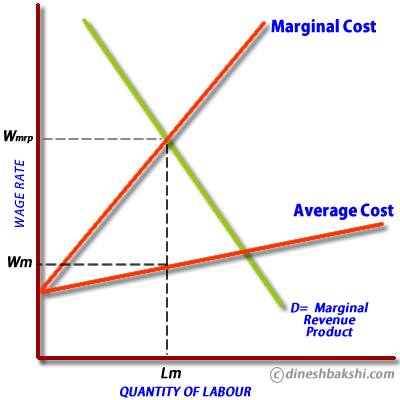
The monoponist will hire workers by equating the marginal cost paid to employ a worker with the marginal revenue product gained from this employment. The wage paid by the monoponist is Wm. This is actually below the wage that should be paid if he was paying the full value of their marginal revenue product, which is Wmrp. The level of employment is Lm.
In this situation the power of the employer in the labour market is of over-riding importance and the employer can set a low wage because of his buying power.





